A – L
Achilles Tendonitis
Achilles tendonitis is inflammation of the Achilles tendon, the largest tendon in the human body. This is generally caused by an overuse injury and is more common among athletes. Achilles tendonitis can also occur within the inactive population when other factors contribute, such as obesity, tight calf muscles and poor shoe gear. Symptoms include pain and swelling to the back of the heel and difficulty walking and participating in activities. Achilles tendonitis is generally slow to heal due to the tendon’s poor blood flow. Treatment includes rest, stretching, icing, anti-inflammatories, compression, heel lifts, immobilization, MLS Laser therapy and physical therapy. If untreated, Achilles tendonitis can lead to tears and rupture of the tendon and heel spurs. This condition can be prevented with regular exercise, stretching and warm-ups before exercise to improve strength and elasticity of the tendon.
Ankle Sprain
Ankle sprains are caused by a twisting injury or force on the ankle joint, often resulting in one or more ligaments of the ankle to be stretched or torn. Ankle injuries occur commonly while playing basketball, slipping on ice, and stepping incorrectly off of a curb. If not properly treated, ankle sprains can develop into chronic conditions. Symptoms include pain, swelling and bruising to the ankle and difficulty walking and participating in activities. X-rays are always taken in the office to rule out fracture and occasionally an MRI is ordered to evaluate the extent of injury to the ankle ligaments. Treatment includes rest, icing, stretching, bracing, MLS Laser therapy, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatories.
Arthritis
Arthritis is a disabling and occasionally crippling disease afflicting almost 40 million Americans. In some forms, it appears to be hereditary. While the prevalence of arthritis increases with age, it can affect people of all ages. Arthritis is most common in those over the age of 50. Arthritis is inflammation and swelling of joint cartilage, generally accompanied by an increase in fluid within the joints. Treatment may include anti-inflammatories, icing, custom orthotics, braces, MLS Laser therapy, steroid injections, and surgery.
Athlete’s Foot
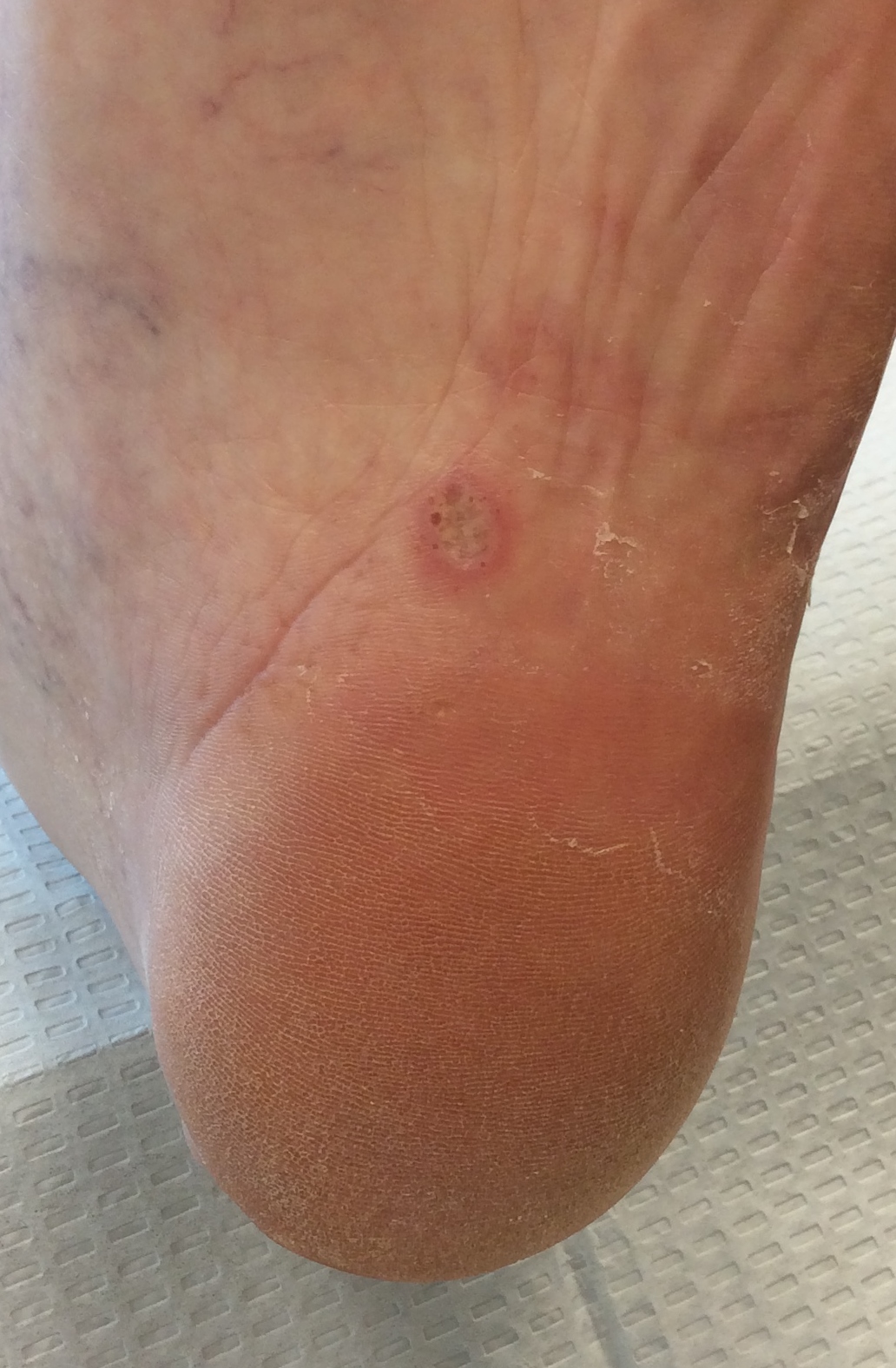 Athlete’s Foot is a fungal infection of the skin, usually occurring between the toes and in the arch of the foot. Fungus affects the feet because shoes create a warm, dark, and humid environment that encourages fungus growth. Symptoms include dry, scaly, red skin with itching, inflammation, and blisters. Fungal infections of the skin can spread to the toenails and vice versa. Treatment includes antifungal creams, ointments, and occasionally oral medication. Athlete’s foot can be prevented by proper hygiene, wearing fresh socks and shoes daily, and avoiding barefoot walking while in public areas such as pools, hotels, and gyms.
Athlete’s Foot is a fungal infection of the skin, usually occurring between the toes and in the arch of the foot. Fungus affects the feet because shoes create a warm, dark, and humid environment that encourages fungus growth. Symptoms include dry, scaly, red skin with itching, inflammation, and blisters. Fungal infections of the skin can spread to the toenails and vice versa. Treatment includes antifungal creams, ointments, and occasionally oral medication. Athlete’s foot can be prevented by proper hygiene, wearing fresh socks and shoes daily, and avoiding barefoot walking while in public areas such as pools, hotels, and gyms.
Blisters
Most blisters of the feet are caused by friction due to shoes or minor burns and do not require medical attention. New skin will form beneath the affected area and the fluid is simply absorbed or can be drained. Do not remove the overlying skin since this acts as a barrier to bacteria. You can soothe blisters with vitamin E ointment or an aloe-based cream. If blisters persist or appear infected, please call to make an appointment right away.
Bone Spurs
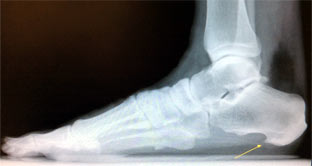 A bone spur is an overgrowth of bone as a result of joint arthritis, trauma, or stress to a ligament or tendon. The growth can cause pain, swelling, and/or restrict joint motion, depending upon the location and size of the spur. Within the foot, spurs are most commonly found on the heel bone due to plantar fasciitis or Achilles tendonitis and within the great toe joint. Your podiatrist will take x-rays to evaluate and determine the best treatment option.
A bone spur is an overgrowth of bone as a result of joint arthritis, trauma, or stress to a ligament or tendon. The growth can cause pain, swelling, and/or restrict joint motion, depending upon the location and size of the spur. Within the foot, spurs are most commonly found on the heel bone due to plantar fasciitis or Achilles tendonitis and within the great toe joint. Your podiatrist will take x-rays to evaluate and determine the best treatment option.
Bunion
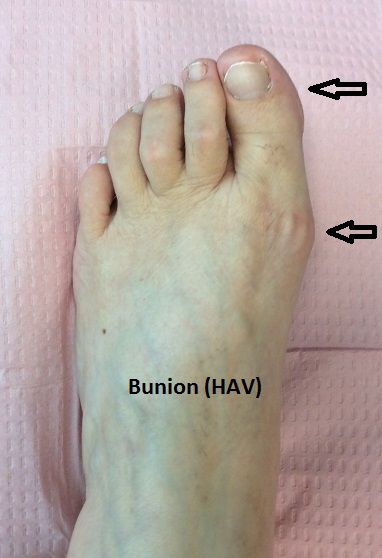 Bunions are a progressive deformity that results from mechanical imbalance and undue stress on the big toe joint. This leads to a bony prominence to the inside of the toe joint and drifting of the great toe causing crowding to the smaller toes. Contrary to popular belief, bunions are aggravated, not caused, by shoes. Bunions are usually an inherited deformity of the foot. Bunions more commonly affect women due to wearing high-heeled or pointed-toed shoes which aggravate the condition. Symptoms include pain at the great toe joint, swelling, redness, corns, calluses, and difficulty wearing shoes. Because bunions are progressive, it is best to see a podiatrist for diagnosis and treatment to correct the problem before severe pain, arthritis, and deformity occur.
Bunions are a progressive deformity that results from mechanical imbalance and undue stress on the big toe joint. This leads to a bony prominence to the inside of the toe joint and drifting of the great toe causing crowding to the smaller toes. Contrary to popular belief, bunions are aggravated, not caused, by shoes. Bunions are usually an inherited deformity of the foot. Bunions more commonly affect women due to wearing high-heeled or pointed-toed shoes which aggravate the condition. Symptoms include pain at the great toe joint, swelling, redness, corns, calluses, and difficulty wearing shoes. Because bunions are progressive, it is best to see a podiatrist for diagnosis and treatment to correct the problem before severe pain, arthritis, and deformity occur.
Calluses
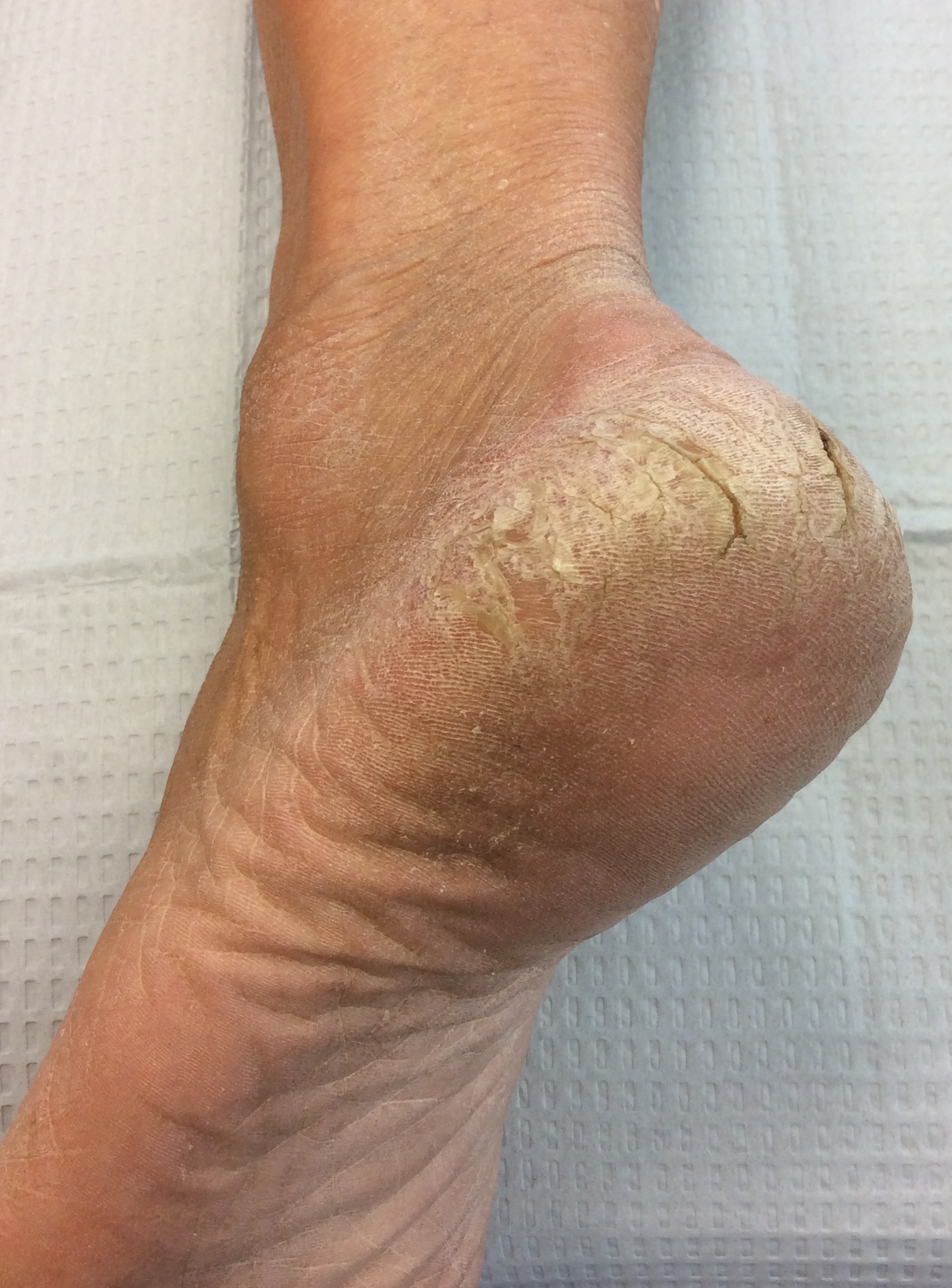 A callus is an area of hard, thickened skin that can occur across the ball of the foot, on the heel, or on the bottom of the big toe. Calluses are caused by pressure and friction to the skin due to deformities of the foot such as bunions, hammertoes, tailors bunions, and high arched foot. Calluses are routinely trimmed by a podiatrist, but do reoccur. To prevent reoccurrence of painful calluses, you and your podiatrist may decide on surgical treatment to correct the foot deformities causing the calluses. They can also be treated with custom orthotics to pad and take pressure off of calluses.
A callus is an area of hard, thickened skin that can occur across the ball of the foot, on the heel, or on the bottom of the big toe. Calluses are caused by pressure and friction to the skin due to deformities of the foot such as bunions, hammertoes, tailors bunions, and high arched foot. Calluses are routinely trimmed by a podiatrist, but do reoccur. To prevent reoccurrence of painful calluses, you and your podiatrist may decide on surgical treatment to correct the foot deformities causing the calluses. They can also be treated with custom orthotics to pad and take pressure off of calluses.
Corns
 A corn is an area of hard, thickened skin that forms on the top or sides of the toes. The surface layer of the skin thickens, irritating the tissues beneath. Corns are caused by rubbing between the toes or to the inside of shoes due to hammer toe deformities. Corns are routinely trimmed by a podiatrist, but do reoccur. To prevent reoccurrence of painful corns, you and your podiatrist may decide on surgical treatment to correct the foot deformity causing the corns.
A corn is an area of hard, thickened skin that forms on the top or sides of the toes. The surface layer of the skin thickens, irritating the tissues beneath. Corns are caused by rubbing between the toes or to the inside of shoes due to hammer toe deformities. Corns are routinely trimmed by a podiatrist, but do reoccur. To prevent reoccurrence of painful corns, you and your podiatrist may decide on surgical treatment to correct the foot deformity causing the corns.
Cysts
Cysts are benign fluid filled masses found under the skin. Common cysts of the feet are known as synovial, ganglion, or mucoid cysts. They can form within or around tendons and joints. These cysts are filled with synovial fluid that has leaked from nearby joints or tendons. These cysts can be drained in the office, but do commonly reoccur. X-rays or MRI may be taken to evaluate the cause of the cyst. If they persist and are symptomatic, they can be removed surgically. If the cyst is not symptomatic it does not require treatment.
Flat Feet or Fallen Arches
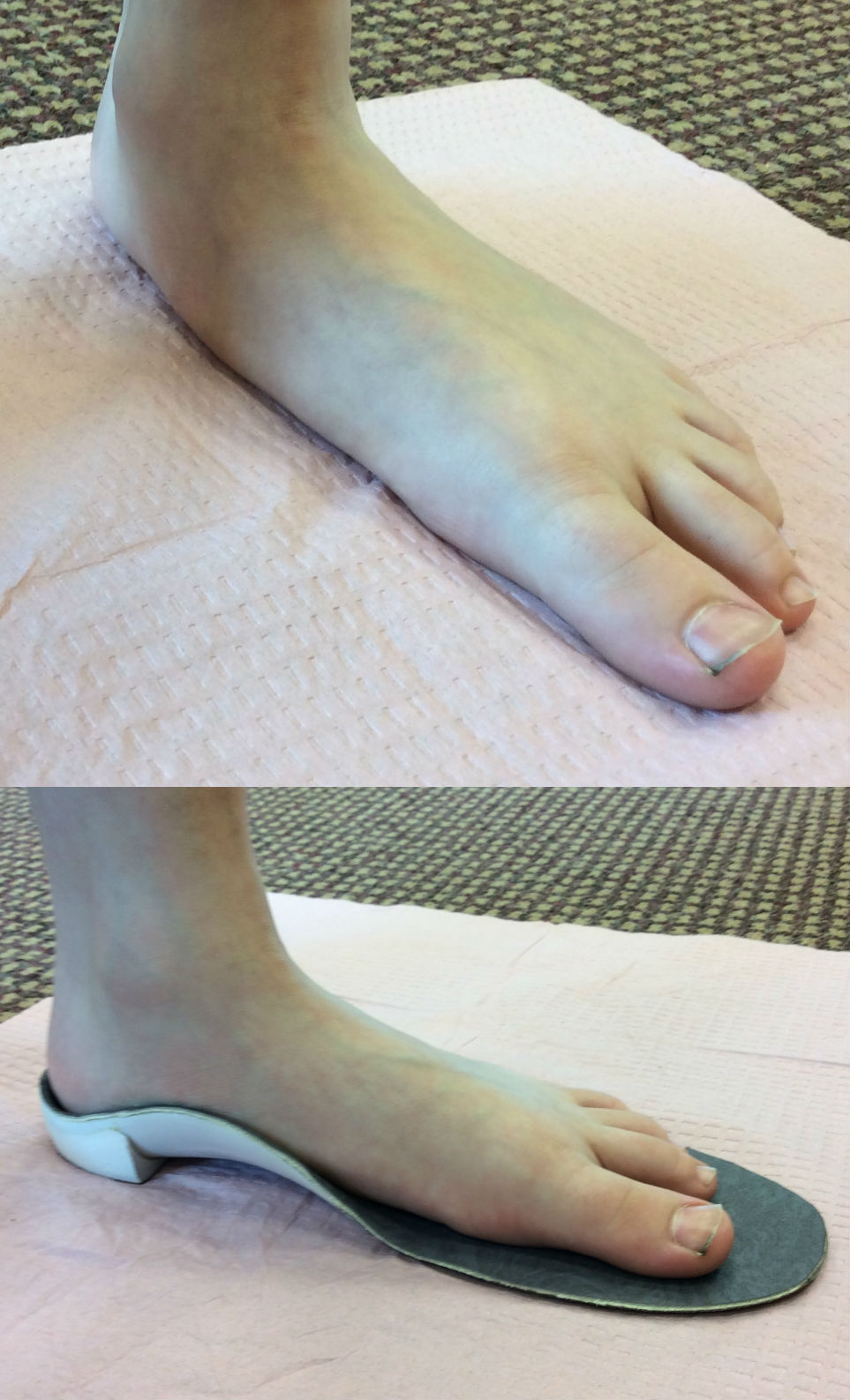 Flat feet have excessive pronation, lower than normal or even non-existent arches. This can cause further foot problems, evenleading to disability with advancing age and increased inactivity. Flat feet are most commonly a hereditary condition. Symptoms may include pain to the foot and ankle, clumsiness, and
Flat feet have excessive pronation, lower than normal or even non-existent arches. This can cause further foot problems, evenleading to disability with advancing age and increased inactivity. Flat feet are most commonly a hereditary condition. Symptoms may include pain to the foot and ankle, clumsiness, and
difficulty wearing shoes. Flatfeet are usually first treated with custom orthotics for arch support and to hold the feet in a healthy position. If orthotics do not provide pain relief and improved function then surgical treatment options are discussed.
Foot Odor
Foot odor is caused by the interaction between your perspiration/sweat and the bacteria that thrives in your shoes and socks. Therefore, any attempt to reduce foot odor has to address both your sweating and your footwear. Odor can also be caused by an inherited condition called hyperhidrosis, or excessive sweating, which primarily affects men. Stress, medications, fluid intake and hormonal changes can also increase the amount of perspiration your body produces. Treatments include foot powders, foot soak tablets, avoiding prolonged use of wet socks, and wearing specific moisture-wicking socks. Alternate between shoes, so they have 24 hours to air dry.
Fungus
Athlete’s foot and fungal nails are the most common types of fungal infections of the foot. The fungus usually attacks the feet because shoes create a warm, dark, and humid environment which encourages fungal growth. The warmth and dampness of areas around swimming pools, showers, and locker rooms, are also breeding grounds for fungus. Other conditions, such as reaction to dyes or adhesives in shoes, eczema, and psoriasis, may mimic Athlete’s foot. Fungal infections are treated with topical and/or oral antifungal medications, laser treatment, and good daily foot hygiene.
Gangrene
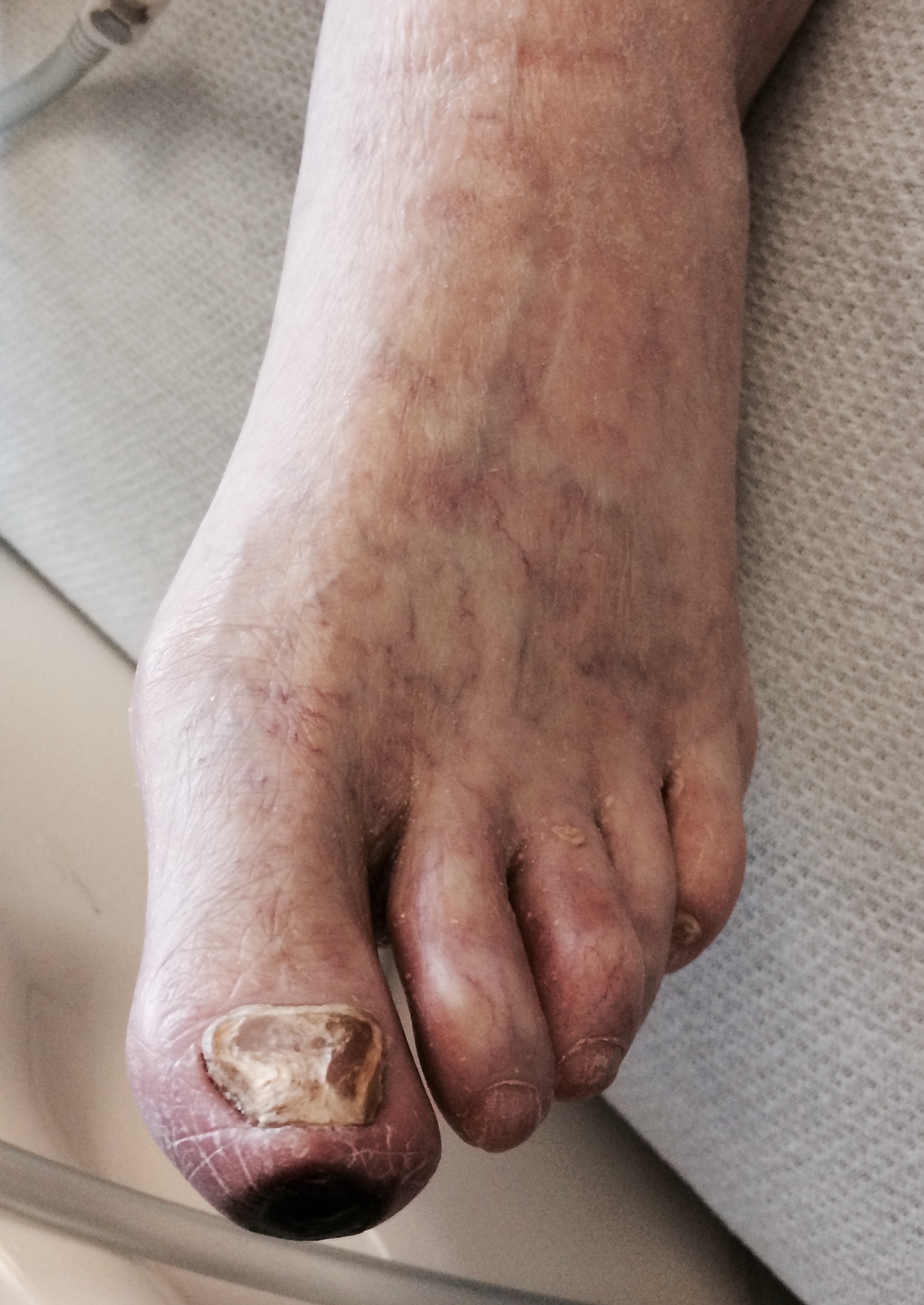 Gangrene is a potential life-threatening condition caused by critically insufficient blood supply to the foot (necrosis). Injury and infections can also lead to gangrene when there is poor blood flow. Long term smoking and those with diabetes are more prone to foot gangrene. Gangrene may be treated with hospitalization, revascularization procedures, wound care, antibiotics, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, and amputation.
Gangrene is a potential life-threatening condition caused by critically insufficient blood supply to the foot (necrosis). Injury and infections can also lead to gangrene when there is poor blood flow. Long term smoking and those with diabetes are more prone to foot gangrene. Gangrene may be treated with hospitalization, revascularization procedures, wound care, antibiotics, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, and amputation.
Gout
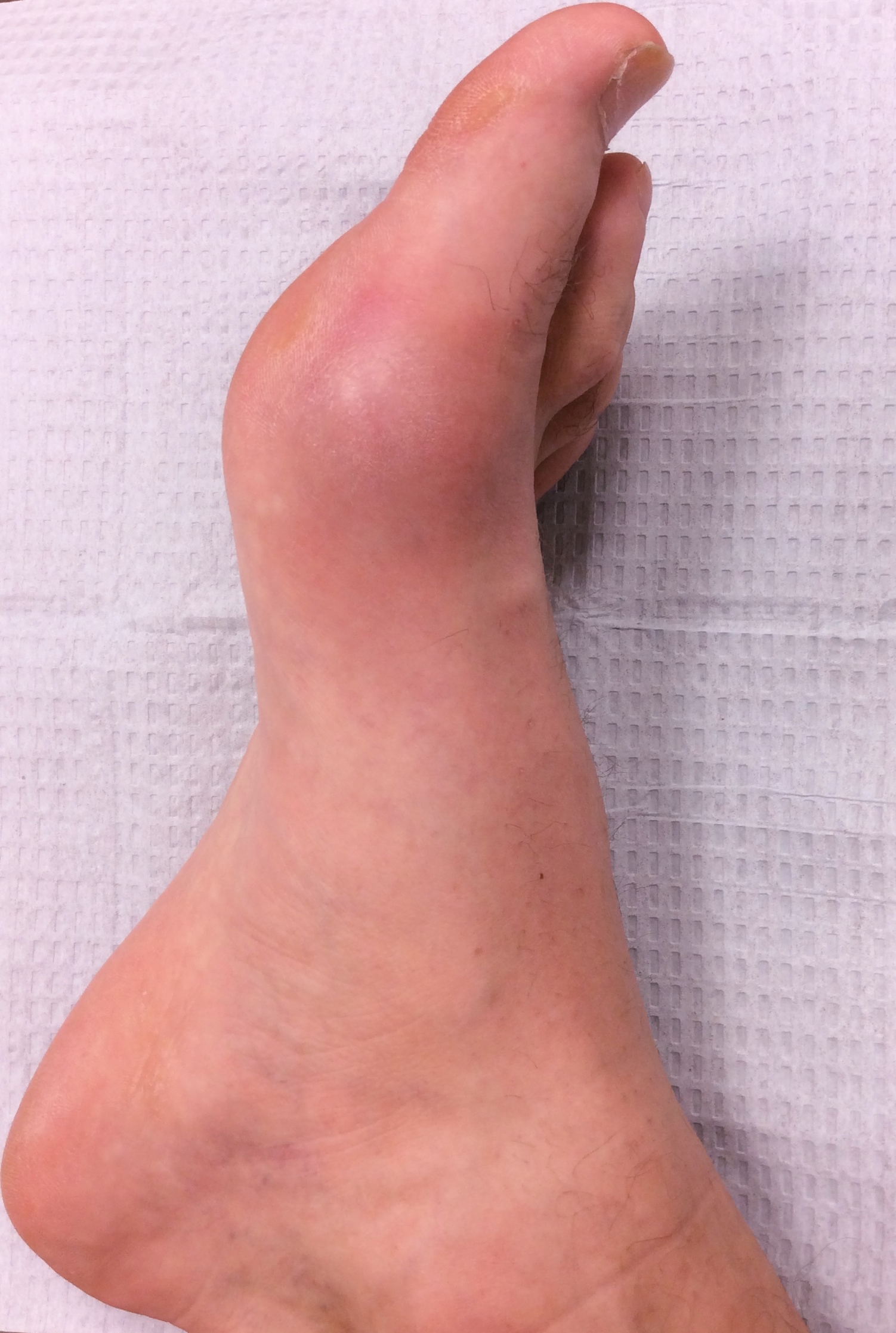 Gout is a form of arthritis caused by a buildup of uric acid, a normal byproduct of the diet, in the joints. The great toe joint and ankle joint are commonly affected areas. Attacks of gouty arthritis are extremely painful, perhaps more so than any other form of arthritis. Men are much more likely to be afflicted than women. Research suggests that diets heavy in red meat, rich sauces, shellfish, and alcohol are associated with gout. However, other protein compounds in foods such as lentils and beans may play a role. Symptoms include severe joint pain, redness, and swelling. Gout can be treated with steroid injections, anti-inflammatories, oral steroids, icing, elevating, and limiting activity.
Gout is a form of arthritis caused by a buildup of uric acid, a normal byproduct of the diet, in the joints. The great toe joint and ankle joint are commonly affected areas. Attacks of gouty arthritis are extremely painful, perhaps more so than any other form of arthritis. Men are much more likely to be afflicted than women. Research suggests that diets heavy in red meat, rich sauces, shellfish, and alcohol are associated with gout. However, other protein compounds in foods such as lentils and beans may play a role. Symptoms include severe joint pain, redness, and swelling. Gout can be treated with steroid injections, anti-inflammatories, oral steroids, icing, elevating, and limiting activity.
Hammertoe
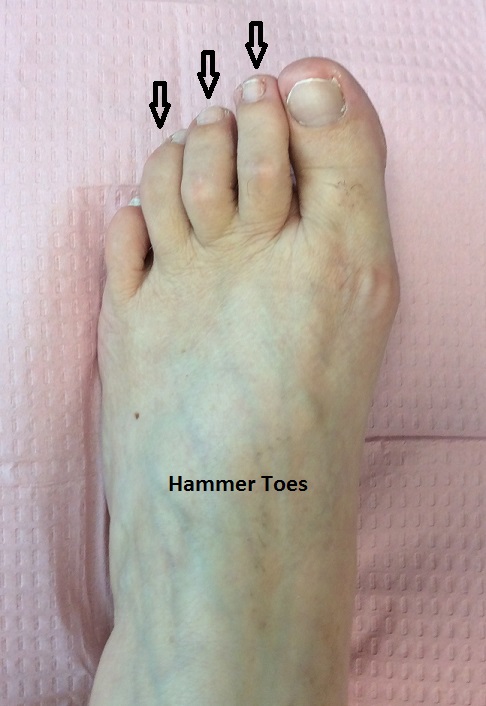 Hammertoes are deformities of the smaller toes of the foot. The middle joint of the toe is bent, resembling a hammer. Hammertoes can cause thickened toenails and corns or calluses on the top of the toe or at the tip of the toe. If diabetic, these corns and calluses can lead to ulceration (sores) and infection. Pain may be experienced to the toes or the ball of the foot. Many people with hammer toes have difficulty finding comfortable shoes. Hammertoes can become painful and rigid or inflexible and require surgical correction.
Hammertoes are deformities of the smaller toes of the foot. The middle joint of the toe is bent, resembling a hammer. Hammertoes can cause thickened toenails and corns or calluses on the top of the toe or at the tip of the toe. If diabetic, these corns and calluses can lead to ulceration (sores) and infection. Pain may be experienced to the toes or the ball of the foot. Many people with hammer toes have difficulty finding comfortable shoes. Hammertoes can become painful and rigid or inflexible and require surgical correction.
Ingrown Nails
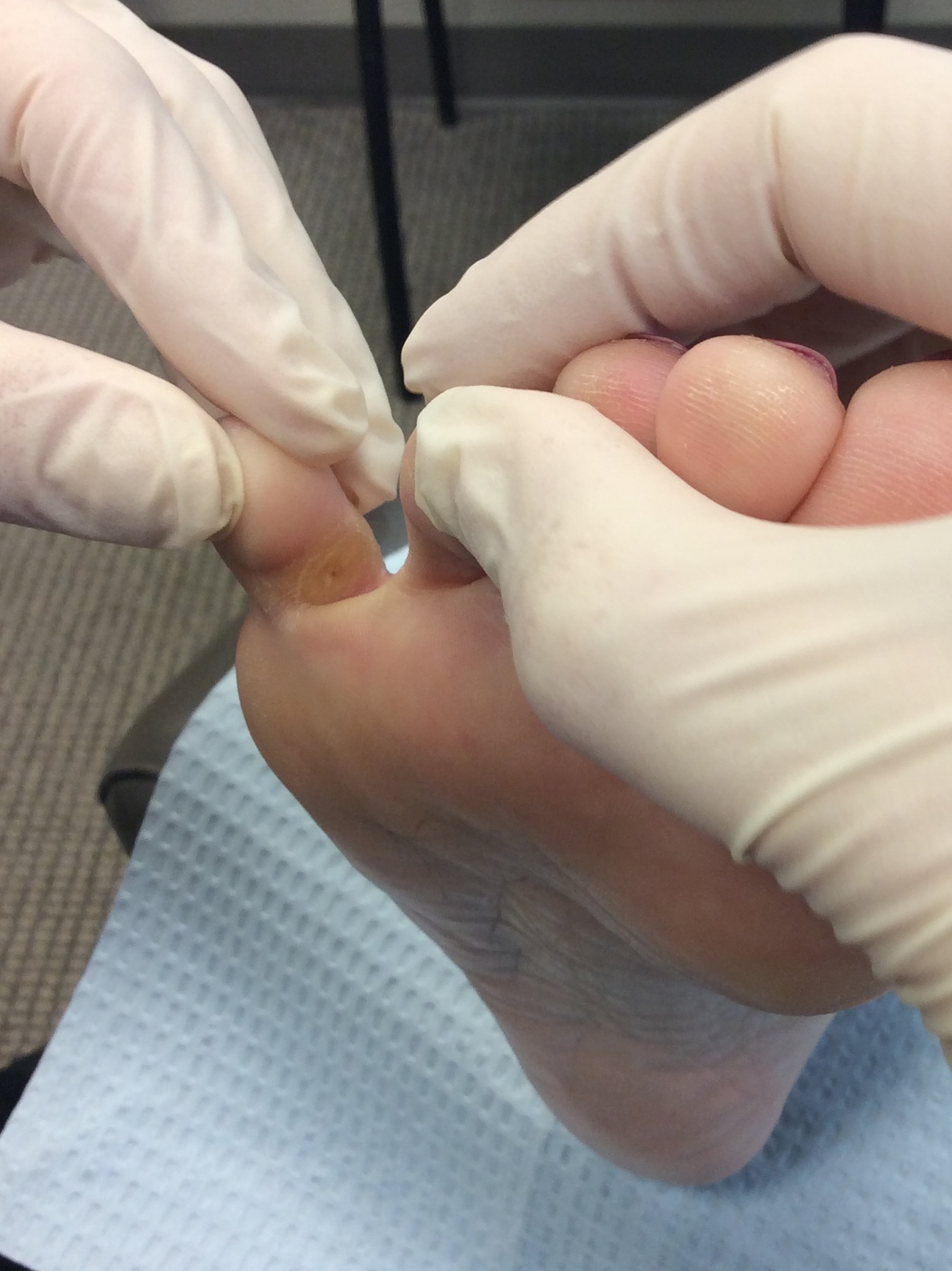
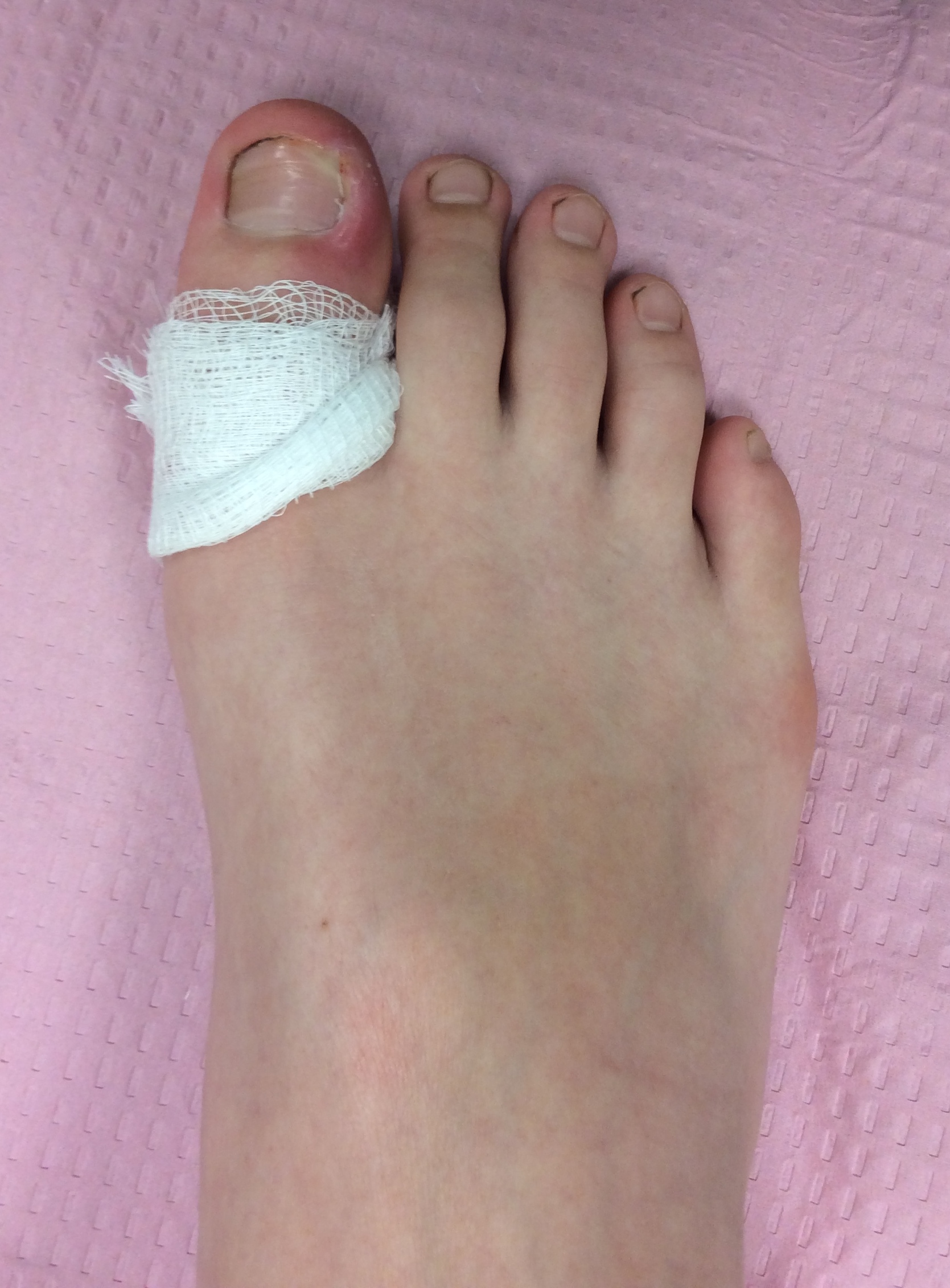 Ingrown toe nails have borders or sides that dig painfully into the skin, often causing infection. They are frequently caused by improper nail trimming, but can also be caused by shoe pressure, injury, fungal infection, and poor foot structure. Infected ingrown toe nails are trimmed and drained under sterile technique with local anesthesia (injections) in the office. If the ingrown toenail is chronic or reoccurring, then a permanent removal of the offending nail border can be performed while keeping the rest of the nail intact.
Ingrown toe nails have borders or sides that dig painfully into the skin, often causing infection. They are frequently caused by improper nail trimming, but can also be caused by shoe pressure, injury, fungal infection, and poor foot structure. Infected ingrown toe nails are trimmed and drained under sterile technique with local anesthesia (injections) in the office. If the ingrown toenail is chronic or reoccurring, then a permanent removal of the offending nail border can be performed while keeping the rest of the nail intact.
Intoed Gait
 Intoed gait (walking pattern) is when the feet turn inward when walking or running. This is caused by abnormal rotation of the legs or hips. Young children normally outgrow this condition, but some require treatment to correct the deformity. Special braces and shoes may be prescribed by your physician. Parents should prevent their children from sitting in the W-shaped position.
Intoed gait (walking pattern) is when the feet turn inward when walking or running. This is caused by abnormal rotation of the legs or hips. Young children normally outgrow this condition, but some require treatment to correct the deformity. Special braces and shoes may be prescribed by your physician. Parents should prevent their children from sitting in the W-shaped position.